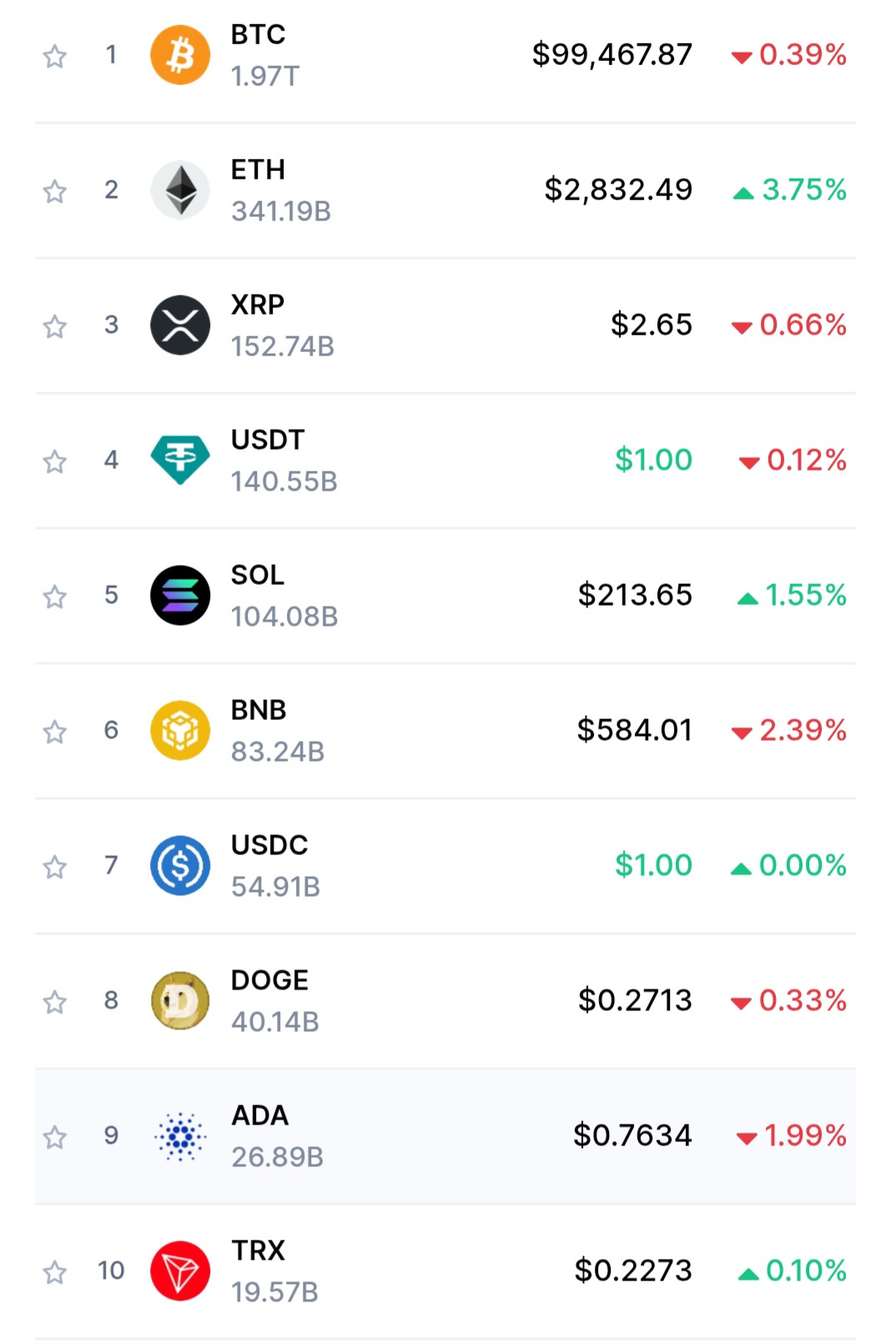
Understanding market trends is like learning to read the pulse of the economy. It’s an essential skill for anyone looking to navigate the financial markets confidently. If you’re new to investing, the idea of deciphering market movements might seem daunting, but with the right tools and mindset, you can start making informed decisions. Let’s embark on this journey together and unravel the art of reading market trends.
What Are Market Trends?
At its core, a market trend is the general direction in which a market is moving over a certain period. Think of it as the market’s mood swings—sometimes optimistic, sometimes cautious, and occasionally indecisive. Recognizing these trends helps investors anticipate potential movements, manage risks, and identify opportunities.
- Uptrend (Bull Market): A series of higher highs and higher lows, indicating growing investor confidence.
- Downtrend (Bear Market): A series of lower highs and lower lows, reflecting a decline in market confidence.
- Sideways Trend (Flat Market): When the market moves within a narrow range, showing neither strong upward nor downward momentum.
Why Reading Market Trends Matters
Understanding market trends isn’t just about predicting the future; it’s about making sense of the present. By recognizing patterns and signals, you can:
- Make Informed Decisions: Identify optimal entry and exit points for your investments.
- Manage Risks: Anticipate potential downturns and adjust your portfolio accordingly.
- Capitalize on Opportunities: Spot emerging market movements before they become mainstream.
Key Indicators to Read Market Trends
To read market trends effectively, you need the right set of tools. Here are some fundamental indicators and concepts that can guide you:
1. Moving Averages
A moving average smooths out price data by creating a constantly updated average price. It’s a simple yet powerful tool.
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Calculates the average price over a specific number of periods.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new information.
How to Use: If the price is above the moving average, it could indicate an uptrend; if it’s below, a downtrend might be in play.
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
RSI measures the speed and change of price movements on a scale of 0 to 100.
- Overbought Conditions: An RSI above 70 may suggest that the asset is overbought and could be due for a correction.
- Oversold Conditions: An RSI below 30 might indicate that the asset is oversold and could be poised for a rebound.
How to Use: Look for divergence between RSI and price to spot potential trend reversals.
3. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
MACD is a momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages.
- Signal Line Crossovers: When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it may indicate a bullish trend; crossing below could suggest a bearish trend.
- Histogram: Represents the difference between the MACD line and the signal line, helping to visualize momentum changes.
How to Use: Use MACD to identify potential buy or sell signals based on momentum shifts.
4. Trading Volume
Volume reflects the number of shares or contracts traded in a security or market.
- Increasing Volume: Confirms the strength of a trend. High volume on price increases suggests strong buying interest.
- Decreasing Volume: May indicate weakening momentum in the current trend.
How to Use: Combine volume analysis with price movements to validate trends.
Fundamental vs. Technical Analysis
Fundamental Analysis
This approach focuses on evaluating an asset’s intrinsic value by examining related economic and financial factors.
- Economic Indicators: GDP growth rates, employment data, and inflation.
- Company Performance: Earnings reports, management effectiveness, and market share.
How to Use: Analyze how macroeconomic factors and company fundamentals could influence market trends.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis concentrates on statistical trends gathered from trading activity.
- Price Patterns: Identifying formations like head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms.
- Chart Types: Line charts, bar charts, candlestick charts.
How to Use: Utilize charts and indicators to predict future price movements based on historical patterns.
Steps to Read Market Trends
Embracing a systematic approach can enhance your ability to interpret market signals:
1. Define Your Time Frame
- Short-Term Trends: Useful for day traders focusing on hourly or daily movements.
- Long-Term Trends: Beneficial for investors with horizons spanning months or years.
Tip: Align your analysis with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
2. Use Multiple Indicators
Relying on a single indicator can be misleading. Combining several tools provides a more comprehensive view.
- Confluence: When multiple indicators point to the same trend, the signal is stronger.
- Diversification: Different indicators can confirm or challenge your initial findings.
Example: If both RSI and MACD suggest a bullish trend, it reinforces the potential upward movement.
3. Analyze Market Sentiment
Understanding the collective mood of investors helps gauge the market’s direction.
- News and Media: Stay informed about global events, earnings reports, and policy changes.
- Social Sentiment: Monitor investor sentiment through forums, social media, and sentiment indices.
How to Use: Be cautious of extreme optimism or pessimism, as markets can reverse when sentiment reaches peaks.
4. Identify Support and Resistance Levels
- Support Levels: Price points where an asset tends to stop falling due to increased buying.
- Resistance Levels: Price points where selling pressure prevents the asset from rising further.
How to Use: Use these levels to make decisions about entry and exit points.
5. Practice Risk Management
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Protect your investments by setting predetermined exit points to limit losses.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread investments across different assets to mitigate risk.
Remember: No analysis is foolproof; always be prepared for unexpected market movements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Navigating market trends involves avoiding pitfalls that can derail your investment journey:
- Emotional Trading: Letting fear or greed dictate decisions can lead to impulsive actions.
- Overcomplicating Analysis: Using too many indicators can create confusion; keep it straightforward.
- Ignoring the Bigger Picture: Focusing solely on short-term movements may cause you to miss long-term opportunities.
- Chasing the Market: Jumping into trends late can result in buying high and selling low.
Practical Tips for Beginners
Start with Education
- Read Books: Explore classics like “Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets” by John J. Murphy.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer courses on market analysis.
Use Demo Accounts
- Practice Trading: Many brokers offer demo accounts to practice without risking real money.
- Test Strategies: Experiment with different indicators and time frames to find what works for you.
Stay Disciplined
- Create a Trading Plan: Define your goals, risk tolerance, and strategies.
- Consistent Review: Regularly assess your performance and adjust as needed.
Stay Informed
- Economic Calendars: Keep track of upcoming events that could impact markets.
- Reliable Sources: Follow reputable financial news outlets for accurate information.
Embrace the Journey
Reading market trends is both an art and a science. It requires patience, continuous learning, and a keen eye for detail. Remember that even seasoned investors are constantly refining their skills. Embrace each experience as a stepping stone towards greater confidence and proficiency in the markets.
A Final Thought: Think of market analysis as learning a new language. At first, it might seem foreign and complex, but with practice and exposure, you’ll start to understand the nuances and communicate fluently. Stay curious, keep exploring, and don’t hesitate to seek guidance when needed.
Looking Ahead: The Power of Continuous Learning
The financial markets are ever-evolving landscapes influenced by a myriad of factors. As a beginner, immersing yourself in ongoing education will empower you to adapt and thrive. Consider exploring topics like:
- Advanced Technical Indicators: Dive deeper into tools like Bollinger Bands and Fibonacci retracements.
- Global Economic Policies: Understand how international events and policies affect market dynamics.
- Behavioral Finance: Study how psychological factors impact investor behavior and market trends.
By investing in your knowledge, you’re not just reading market trends—you’re writing your own success story in the world of investing.

 Previous Post
Previous Post